This year has been monumental for the cryptocurrency sector in terms of mainstream adoption. A recent report published by Grayscale Investments found that more than one-quarter of United States investors (26%) surveyed own Bitcoin (BTC), up from 23% in 2020. With the holidays around the corner, financial services provider MagnifyMoney also found that nearly two-thirds of surveyed Americans hope to receive cryptocurrency as a gift this year.
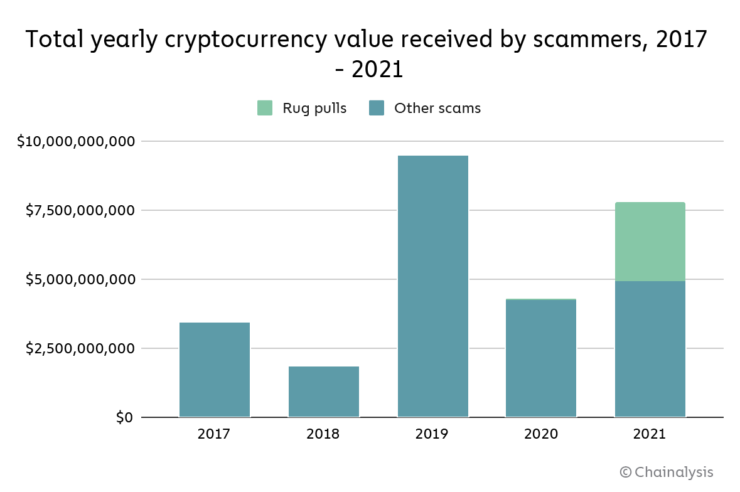
While crypto’s growth is notable, there has also been an increase in the number of scams associated with digital assets. A Chainalysis blog post highlighting the company’s “2022 Crypto Crime Report” revealed that scams were the dominant form of cryptocurrency-based crimes by transaction volume this year. The post notes that over $7.7 billion worth of cryptocurrency has been taken from scam victims globally. According to Chainalysis’ previous research, this number represents an 81% increase compared to 2020, a year in which scamming activity dropped significantly compared to 2019.


Scams are the biggest threat for building trust in crypto
Kim Grauer, head of research at Chainalysis, told Cointelegraph that while there are many different crypto-related crimes, scamming has become the largest in terms of value received by criminals. She added that scams represent a significant threat to building trust within the crypto ecosystem, as this may prevent people from investing in digital assets.
Grauer further mentioned that scams related to decentralized finance (DeFi) have been on the rise this year. With an annualized revenue in all DeFi protocols estimated at around $5 billion, this shouldn’t come as a surprise. More interesting, though, is that Chainalsyis has discovered that “rug pulls” have contributed to this year’s increase in scam revenue. According to Grauer, Chainalysis defines rug pulls as an instance when a person or developer decides to unexpectedly cease a project and run away with funds:
“Rug pulls have accelerated the amount of scamming the crypto space has seen this year. In addition to financial scams, rug pulls have exploited different vulnerabilities in the crypto space. Overall, they have taken $2.8 billion of cryptocurrency.”
Although rug pulls are a relatively new crime, Grauer believes these cases are becoming common in the growing DeFi ecosystem. To put this in perspective, the Chainalysis blog post notes, “Rug pulls have emerged as the go-to scam of the DeFi ecosystem, accounting for 37% of all cryptocurrency scam revenue in 2021, versus just 1% in 2020.”
The Chainalysis blog post also provides examples of some of the biggest rug pulls of 2021. For instance, the AnubisDAO case is mentioned as the second-biggest rug pull of this year, with over $58 million worth of cryptocurrency stolen. According to the post, AnubisDAO launched on Oct. 28, 2021, with claims of offering a decentralized currency backed by a number of assets. However, the project didn’t contain a website or white paper, and all of the developers went by pseudonyms. Miraculously, AnubisDAO still managed to raise nearly $60 million overnight, yet 20 hours later, all of those funds disappeared from AnubisDAO’s liquidity pool.
While AnubisDAO demonstrates a large-scale DeFi rug pull, new cases are occurring almost daily. An early Ethereum and DeFi investor who wishes to remain anonymous told Cointelegraph that they fell victim to a rug pull on Dec. 19, 2021. The anonymous source shared that the project is called “up1.network,” noting that many early Ethereum investors were discussing Up1 in a Discord chat group. They added:
“People I trusted were mentioning the project so I checked it out. I thought it was strange to see Up1 giving away airdrops, but thought it could have been affiliated with a DeFi token I had. I then connected my MetaMask wallet and clicked on ‘get airdrop’ but kept getting an error message. I did this three times, which gave the project access to my account.”
Unfortunately, once Up1 gained access to their account, three DeFi tokens worth $50,000 were instantly taken. “I revoked access after the fact on Etherscan so they couldn’t steal any more tokens,” they mentioned. The Ethereum investor then checked the DeFi platform Zerion where they saw the notifications that the DeFi tokens had left their wallet. Zerion also provided them with a wallet address to where the funds went, along with a message:
“0xc28a580acc42294787f44cffbaa788eaa4958056; You gave a web3 site / smart contract unlimited access to your funds (check who you gave access to and revoke here).”
While both AnubisDAO and Up1 are examples of DeFi rug pulls, it’s important to point out that the nonfungible token (NFT) ecosystem is also vulnerable to rug pulls. Most recently, the Bored Ape Yacht Club community fell victim to a rug pull when some members decided to connect their wallets to mint NFTs from a link posted in the group’s Discord channel.
Even more surprising is that rug pull scams are also targeting mainstream NFT projects. For example, on Oct. 28, 2021, the global beauty pageant Miss Universe sent out an official tweet announcing the launch of its NFTs on the Wax blockchain. Unfortunately, the people who minted these nonfungible tokens were part of a rug pull.
As a reminder: DON’T MINT from the links posted in Discord.
Due to amazing members of the community, we’ve obtained pertinent information about the hackers.
We’re working diligently to fix this. Priorities are restoring the server, prosecuting, and making it up to the minters
— Jenkins The Valet (@jenkinsthevalet) December 21, 2021
Jessica Yang, an NFT photographer, told Cointelegraph that when Miss Universe announced the launch of an NFT project, she didn’t question whether it was a scam or not because the pageant is widely known. “The price of each NFT was 0.06 Ethereum. That translates to around $230 for one. The artwork also has the beauty contestant’s face and country they are associated with plastered on it,” she remarked.
Yang also mentioned that the project was geared toward women, noting that Paula Shugart, the president of Miss Universe, previously stated:
“Miss Universe is going to be the first brand in the NFT space that is about women, about women’s empowerment, and embracing the technology, and moving forward. I love it; this is the first one that is away from other more male-oriented spaces.”
Given the brand’s reputation and appeal, Yang and many others minted Miss Universe NFTs, connecting their wallets to the platform. Yet Yang noted that the next day, Miss Universe deleted its official Instagram account. She then noticed that her funds disappeared entirely. Yang added:
”One red flag I saw was coming from their Discord. The moderators kept trying to get everyone to buy Miss Universe NFTs, promising that they were going along with the roadmap. Their roadmap promised monthly AMAs, signed prints, and much more. Even Steve Harvey vetted the project.”
Do your own research
As the DeFi and NFT ecosystems continue to mature and grow, these environments will, unfortunately, be prone to rug pull scams until industry solutions are developed. In the meantime, the best course of action is for users to do their own research.
For instance, Grauer shared that every DeFi project should have a code audit available to make investors feel safer. “Many of the DeFi platforms that have been hacked don’t have code audits,” she remarked. The Chainalysis blog post also pointed out that “rug pulls are prevalent in DeFi because with the right technical know-how, it’s cheap and easy to create new tokens on the Ethereum blockchain or others and get them listed on decentralized exchanges (DEX) without a code audit.”
In addition to code audits, the anonymous Ethereum investor shared that after reviewing the Up1 site more closely, they could tell that it was fake. “For instance, the team was all anonymous, with just first names that couldn’t be clicked on to open a Twitter or LinkedIn profile.” Even with these precautions the anonymous source mentioned that wallet providers also need to do a better job of keeping users safe:
“If there is a questionable site, wallets should seek them out. I believe this technology can scale, but it has to be able to handle these scams. Otherwise, people will lose all their money.”
Following the Up1 rug pull, the anonymous source contacted MetaMask and shared that they got a response noting that it would flag the website.
It’s also important to point out that while a clear industry solution is yet to be developed, Grauer noted that, unlike fiat-related crimes, crypto payments can be traced to their source. With this in mind, she added that some cryptocurrency platforms are starting to take action to keep users safe from scams.
For example, crypto exchange Luno partnered with Chainalysis in 2020 to protect against a scam targeting South African crypto users. Eva Crouwel, head of financial crime at Luno, told Cointelegraph that one of the requirements from a regulatory framework point of view is to be able to monitor and act upon transactions that have a suspicion of money laundering, terrorist financing, sanctions or any other type of illicit activity. She noted that on-chain transactions must be monitored, as well as the design and the development of case management and user interface.
In terms of crypto investors keeping themselves safe from scams, Crouwel recommends staying away from offers that sound too good to be true, adding:
“Start by doing as much due diligence as possible. Look at the company’s/token’s social media profiles to see what other users’ experiences have been. You should also go through the company directors’ personal social media pages and look into their industry connections and employment background so ensure their history is sound.”


















Comments (No)