The metaverse and NFTs have influenced the digital world as well as industries spanning from art to gaming to even investing. However, these industries have yet to attain their full potential.
Twitter, Meta, and Reddit are all working on NFT or Metaverse projects, investors are betting big on NFTs, and new companies are cropping up.
So, how do the metaverse and NFTs’ future look? What industry will they disrupt next? And what developments will define the next few years? Let’s look at five emerging trends within the metaverse and NFT spaces.
1. Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality (AR) will reduce entry barriers into the metaverse because AR-compatible devices are cheaper to acquire and use. Anyone can use their smartphone to access AR features. One example is Pokemon GO which had over 1.1 million cumulative app downloads in 2020.
Augmented reality is currently in its early stages, but it will mature in the future years. It is a novel method that will bring value to daily life. The worldwide augmented reality industry is estimated to expand in the following years, with a market valuation of up to $300 billion by 2024.
Several businesses are developing augmented reality (AR) solutions for their clients. Apple, for example, is working on an AR/VR headset. The manufacturing schedule was initially pushed back from 2020 to 2022; however, rumors say the tech giant has completed crucial production testing.
2. Metaverse Land
After the social media behemoth, Facebook changed its name to Meta and declared its plan to invest in the virtual reality field, interest in augmented reality, virtual reality, and metaverse real estate skyrocketed.
Nonetheless, pieces of land in the virtual real estate market may seem unusual investments. The fact is that they are, in many respects, extremely comparable to real-world real estate. According to recent research by crypto asset management Grayscale, the digital world might soon become a $1 trillion enterprise.
Investors prefer metaverse-based real estate due to multiple reasons. For starters, virtual property, like physical property, is in short supply. Owning virtual real estate means you have a unique piece of land in a metaverse environment that you may use to create income-generating assets like leasable buildings or virtual spaces with sponsored events.
Second, each piece of metaverse real estate is unique and protected by a non-fungible token (NFT). An NFT is a deed or evidence of ownership for anything digital (or physical).
Your virtual real estate NFT ensures your ownership and enables you to sell the property to a different owner. It also records all transactions for that property, removing the need for title work. It is essentially a digital act from the 21st century.
3. Solana NFTs
NFTs function similarly to blockchain-backed receipts for digital assets like artwork, profile photographs, collectibles, and more. Last year, the NFT market produced around $25 billion in trade volume, with Ethereum and its sidechain and layer-2 scaling solutions well ahead of the competition.
However, the Solana NFT ecosystem has been growing in popularity over the past year and with total sales volume reaching over $1 billion. This increased activity attracted attention from leading Ethereum-based NFT platforms.
OpenSea, the most popular NFT marketplace, added support for collections from the second-largest NFT ecosystem outside of Ethereum with the inclusion of Solana. The integration is currently in beta according to the NFT marketplace.
The moment you’ve been waiting for… @Solana is officially on OpenSea – starting today, with our initial beta!https://t.co/VjhqeGHZxc
— OpenSea (@opensea) April 6, 2022
Although OpenSea claims to support 165 collections, a search of the marketplace by chain reveals that more than 1,175,371 Solana NFTs are listed on the platform. Rarible also decided to add Solana support to their platform following this announcement.
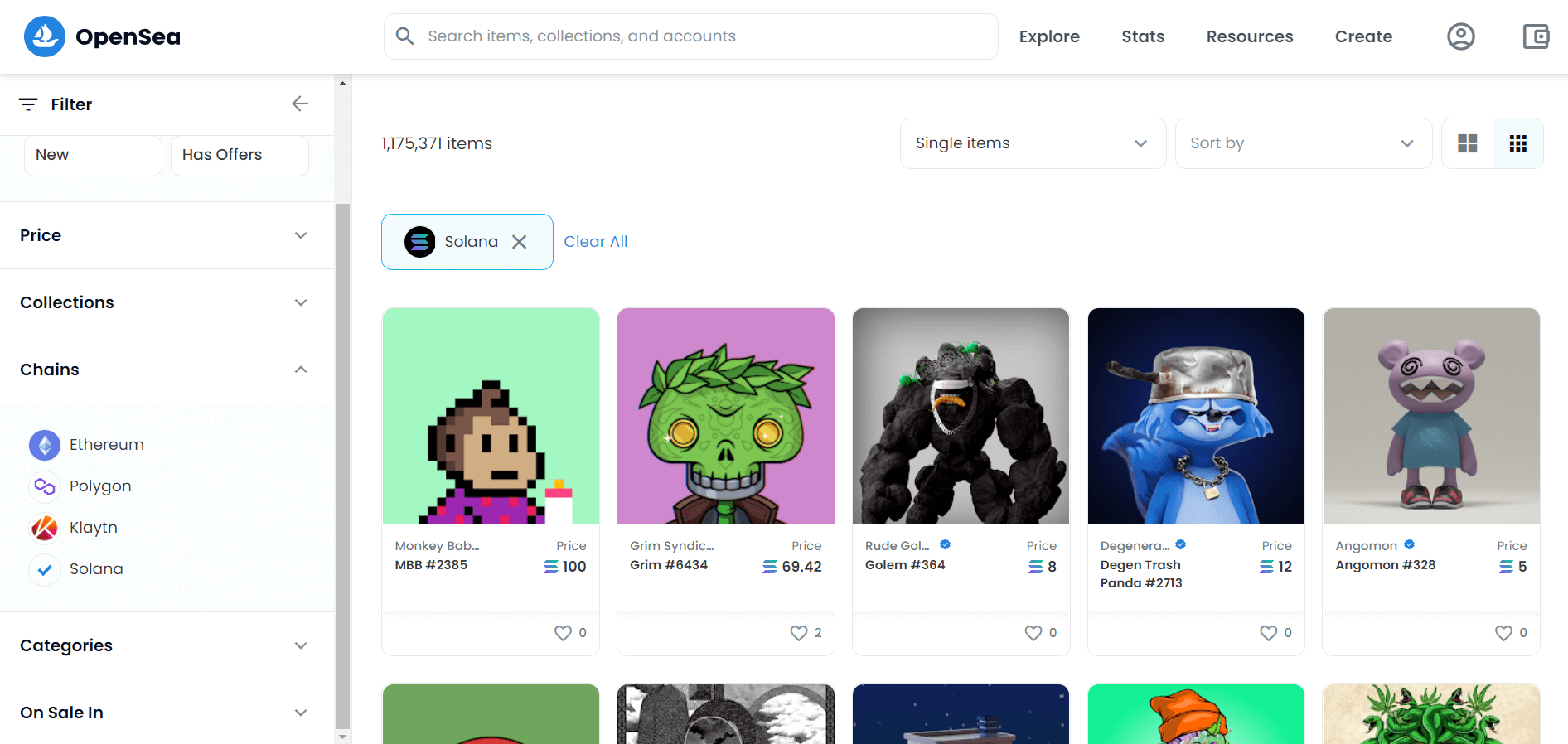

NFT marketplaces that dominate the Solana NFT space include Solanart and DigitalEyes, while projects like SolSea and Magic Eden are relative newcomers.
Magic Eden has had a total sales volume of $41 million in the past month. While this is a small fraction of the $2.5 billion traded on OpenSea last month, Magic Eden had over 95,000 active users in that time.
4. Metaverse Events
Increased accessibility is a significant driver of metaverse occurrences. To begin with, contrary to popular belief, anyone can participate in a virtual reality event. Modern web browsers are powerful, and with the right web platform, the metaverse is accessible with a simple click of a link on any mobile or laptop device.
This kind of accessibility contributes to the democratization of the online environment by guaranteeing that no member of society is unable to access and embrace an online ecosystem owing to technological limitations.
Also, there are no attendance constraints in a virtual environment. Event organizers are not constrained by venue capacity or design, allowing for infinite scalability.
Metaverse venues are customizable to meet the specific demands of an individual event or conference, with access to things like breakout rooms and smaller areas if many lectures or presentations need to take place simultaneously. Unlimited capacity might also imply unrestricted monetization.
One example is MultiNFT, a metaverse platform that holds metaverse-based clubbing events through virtual nightclubs on VR platforms like Decentraland and Somnium Space.
5. Play-to-Earn Gaming
Play-to-earn games have upended the traditional gaming business by enabling players to earn NFTs by achieving predetermined tasks while playing games.
According to Blockchain Gaming Alliance statistics, 1.4 million Unique Active Wallets (UAW) were interacting daily with game dapps (decentralized apps), accounting for 49% of the industry’s total usage in 2021.
The play-to-earn concept has changed the gaming business by enabling gamers to trade and exchange assets between platforms. In-game assets had no real-world worth before the introduction of play-to-earn games because the creators owned and controlled all of the assets in the game.
Players would pay top cash for a game’s most valuable assets, like weapons and skins, but they could only utilize them in-game. They couldn’t move them or exchange them for other assets. When the developer changes the game’s structure, and the assets become outdated, the players lose their investment and must obtain new assets to continue playing the game.
Traditional games were simply for pleasure and excitement in this manner. The inclusion of blockchain and cryptocurrencies resulted in NFTs, which in turn resulted in GameFi.
GameFi has enabled players to increase the value of their assets and earn money while playing their favorite games.
Conclusion
The metaverse and NFTs are two reasonably new yet impactful sectors in the crypto space. As the market matures, we will likely see more technologies, integrations, and products emerge within these industries.




















Comments (No)